SUD medical abbreviation pregnancy – Substance use disorder (SUD) during pregnancy poses significant risks to both the mother and the developing fetus. Understanding the medical implications of SUD, the effects of common substances of abuse, and the available screening, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for healthcare providers and expectant mothers alike.
This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of SUD in pregnancy, exploring its impact on prenatal care, labor and delivery, and postpartum recovery. We’ll also discuss the ethical considerations involved in managing SUD during pregnancy and the importance of prevention and education.
1. Define SUD and its Medical Implications in Pregnancy
Substance use disorder (SUD) is a chronic, relapsing brain disease that involves compulsive use of substances despite negative consequences. During pregnancy, SUD poses significant risks to both the mother and the fetus.
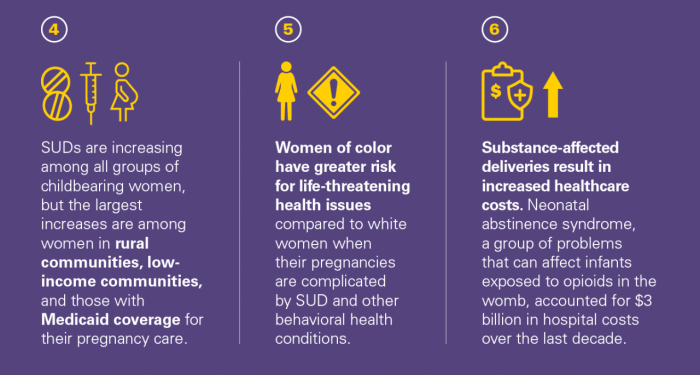
Maternal risks associated with SUD include preterm birth, low birth weight, placental abruption, and maternal death. Fetal risks include fetal alcohol syndrome, developmental delays, and birth defects.
SUD can also affect prenatal care, labor, delivery, and postpartum recovery. Pregnant women with SUD may be less likely to seek prenatal care, and they may experience complications during labor and delivery, such as premature rupture of membranes and prolonged labor.
2. Common Substances of Abuse and Their Effects on Pregnancy
Alcohol
- Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is a group of birth defects that can occur in children whose mothers drink alcohol during pregnancy.
- FAS can cause a range of physical and mental problems, including facial deformities, growth retardation, intellectual disability, and behavioral problems.
Tobacco, SUD medical abbreviation pregnancy
- Smoking during pregnancy increases the risk of preterm birth, low birth weight, and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
- Tobacco smoke contains chemicals that can damage the developing fetus’s organs and tissues.
Opioids
- Opioid use during pregnancy can lead to neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), a condition that occurs when a newborn baby withdraws from opioids after birth.
- NAS can cause a range of symptoms, including seizures, tremors, and respiratory distress.
Stimulants
- Stimulant use during pregnancy can increase the risk of preterm birth, low birth weight, and congenital heart defects.
- Stimulants can also cause anxiety, insomnia, and other problems in pregnant women.
3. Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment of SUD in Pregnancy

Screening for SUD during prenatal care is important to identify women who need treatment. Screening can be done through a variety of methods, including self-report questionnaires, urine drug tests, and blood tests.
Diagnosis of SUD is based on a clinical evaluation by a healthcare provider. Treatment for SUD during pregnancy may include medication, therapy, and support groups.
Medication can be used to manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Therapy can help pregnant women to learn about SUD and develop coping mechanisms. Support groups can provide pregnant women with a safe and supportive environment to share their experiences and learn from others.
4. Long-Term Outcomes for Children Exposed to SUD in Utero

Children who are exposed to SUD in utero may experience a range of long-term developmental, behavioral, and health problems.
These problems can include intellectual disability, learning disabilities, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and behavioral problems.
Children who are exposed to SUD in utero are also at increased risk for chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, stroke, and cancer.
5. Ethical Considerations in SUD and Pregnancy
The management of SUD during pregnancy raises a number of ethical challenges.
These challenges include the balance between the rights of the mother and the well-being of the fetus, the role of healthcare providers in providing non-judgmental and compassionate care, and the need to protect the confidentiality of pregnant women with SUD.
6. Prevention and Education for SUD in Pregnancy
Prevention of SUD during pregnancy is important to protect the health of both the mother and the fetus.
Prevention efforts should focus on education and awareness campaigns, as well as providing support for women at risk of SUD during pregnancy.
Education and awareness campaigns can help to reduce the stigma associated with SUD and increase awareness of the risks of substance use during pregnancy.
Support for women at risk of SUD during pregnancy can include counseling, support groups, and other services that can help women to avoid or reduce substance use.
Ultimate Conclusion: SUD Medical Abbreviation Pregnancy
Managing SUD in pregnancy requires a multidisciplinary approach that prioritizes the well-being of both the mother and the child. Through early intervention, comprehensive treatment, and ongoing support, we can improve outcomes for families affected by SUD and give every child the opportunity to thrive.
FAQ Section
What are the most common substances of abuse during pregnancy?
Alcohol, tobacco, opioids, and stimulants are among the most commonly abused substances during pregnancy.
How can SUD affect prenatal care?
SUD can lead to missed appointments, poor nutrition, and inadequate prenatal care, which can increase the risk of complications for both the mother and the fetus.
What are the ethical considerations involved in managing SUD during pregnancy?
Healthcare providers must balance the rights of the mother with the well-being of the fetus, ensuring that both receive appropriate care and support.